Mobile applications have become an essential element of our daily lives in our quickly changing digital ecosystem. From communication to entertainment, productivity to banking, it appears like there is an app for every facet of our lives. However, when we delve deeper into the future possibilities, it becomes clear that the current state of mobile apps has limitations. While mobile apps have unquestionably transformed the way we engage with technology, they frequently suffer from a lack of compatibility, centralization, and privacy problems.
Enter Web 3.0, a notion with the potential to completely change the app environment as we know it. Web 3.0, also known as the decentralized web or the semantic web, envisions a future in which data, apps, and services are not only linked but also controlled by users. It represents a paradigm change toward an internet that is more open, transparent, and user-centric. Web 3.0 has the ability to address the constraints of mobile apps while ushering in a new era of innovation and possibilities by merging these technologies.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the intriguing realm of Web 3.0 and look at how it affects mobile apps. We’ll look at how Web 3.0 can change the way we engage with apps, promote seamless interoperability, improve user privacy and data ownership, and foster a more collaborative and inclusive digital economy.
Understanding Web 3.0
The term “Web 3.0” refers to the World Wide Web’s upcoming generation which is still in development. Although there is no single, accepted definition of Web 3.0, it is commonly understood to refer to a more decentralized, linked, and user-centric web experience than its forerunners. The following are some significant attributes and Web 3.0-related technologies:
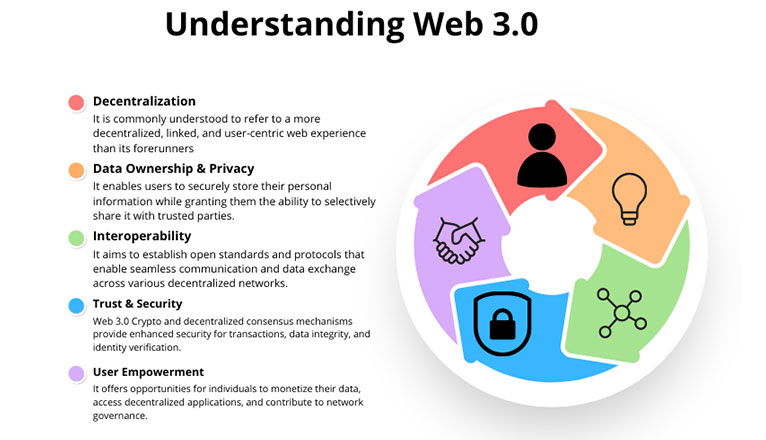
1. Decentralization
Decentralization is booming these days and in 2023, it is anticipated that the DeFi market will generate US$16,960.00m in revenue. Web 3.0 emphasizes decentralization, aiming to distribute power and authority away from centralized entities. It leverages blockchain technology and decentralized networks to enable peer-to-peer interactions, removing the need for intermediaries and increasing transparency.
2. Data Ownership & Privacy
Web 3.0 seeks to give individuals ownership and control over their data. It enables users to securely store and manage their personal information while granting them the ability to selectively share it with trusted parties. Privacy is prioritized, ensuring user data is protected and not exploited without consent.
3. Interoperability
Web 3.0 promotes interoperability between different platforms, applications, and systems. It aims to establish open standards and protocols that enable seamless communication and data exchange across various decentralized networks. This interoperability fosters collaboration, innovation, and a more connected online experience.
4. Trust & Security
Web 3.0 places a strong emphasis on trust and security. Web 3.0 Crypto and decentralized consensus mechanisms provide enhanced security for transactions, data integrity, and identity verification. Smart contracts and decentralized governance frameworks also contribute to building trust among participants in the Web 3.0 ecosystem.
5. User Empowerment
Web 3.0 focuses on empowering users by giving them greater control, agency, and participation. It offers opportunities for individuals to monetize their data, access decentralized applications (dApps), and contribute to network governance. Web 3.0 aims to create a more inclusive and participatory online environment.
Explaining the Shift from Centralized to Decentralized Systems
The transition from centralized to decentralized systems refers to a change in the distribution of power, control, and decision-making within a system or network. In a centralized system, authority and control are concentrated in a single entity or small group of entities known as the central authority. This central authority has the authority to make decisions, enforce regulations, and oversee the operation of the system.
However, there has been a growing movement toward decentralization in numerous fields in recent years, spurred by technological developments and a desire for improved transparency, security, and user empowerment. Decentralized systems transfer power and control throughout a network of individuals, eliminating the need for a centralized authority. Decisions are frequently made through consensus techniques or distributed protocols. Several important elements are contributing to the shift toward decentralized systems:
- Trust and Security
- Transparency
- Resilience Redundancy
- Empowerment Ownership
- Innovation Collaboration
Technologies Enabling Web 3.0
Web 3.0, also known as the decentralized web, aims to transform the internet by incorporating decentralized technologies and principles. Several key technologies are enabling the development and evolution of Web 3.0. Here are some of the prominent ones:
1. Blockchain
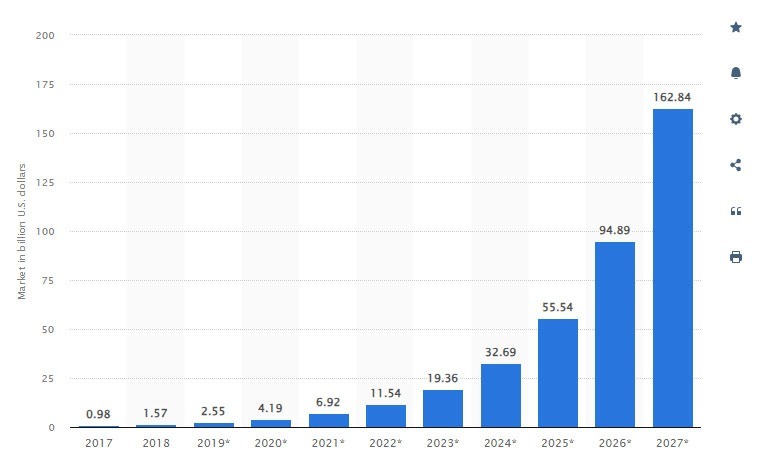
Blockchain is a pretty popular technology these days as studies shoes that in 2018, the global blockchain market was estimated to be worth 1.57 billion dollars, and by 2027, that amount is expected to have increased more than one hundredfold to 163 billion dollars. Blockchain technology plays a central role in Web 3.0 by providing a decentralized and secure infrastructure for applications. It enables transparent and tamper-resistant data storage, smart contracts, and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Polkadot, and Cardano are widely used for building Web 3.0 applications.
2. Cryptocurrencies & Tokens
Web 3.0 relies on digital currencies and tokens that facilitate peer-to-peer transactions and incentivize participation within decentralized networks. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as utility tokens, are integral to the functioning of decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
3. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
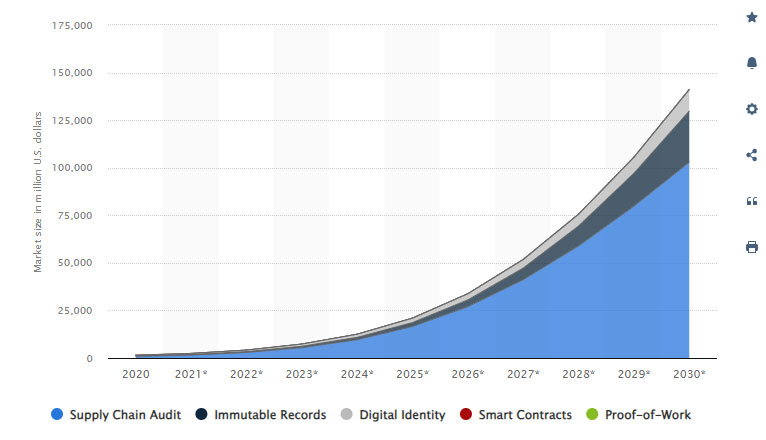
DLT expands beyond blockchain and encompasses various technologies that enable decentralized and distributed data management. DLT allows multiple participants to maintain a shared, synchronized, and immutable ledger without relying on a central authority. This technology enables greater transparency, data integrity, and trust in Web 3.0 applications. Talking about the popularity, by 2030, the globally distributed ledger market is expected to reach a value of over 103 billion US dollars, up more than 102 billion from the previous year.
4. Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized identity (DID) systems offer self-sovereign identity solutions that allow individuals to control their digital identities securely. These systems give users ownership of their personal data and enable seamless authentication and authorization across different applications and platforms without relying on centralized authorities.
5. IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
IPFS is a decentralized protocol for storing and sharing files in a distributed network. It replaces the traditional client-server model with a peer-to-peer network, making content retrieval more efficient and resistant to censorship. IPFS plays a crucial role in Web 3.0 by providing decentralized and permanent storage for dApps, decentralized social networks, and content-sharing platforms.
6. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are organizations governed by smart contracts and operate without a central authority. They enable decentralized decision-making, resource allocation, and community governance. DAOs use blockchain technology to ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in their operations.
The Impact of Web 3.0 on Mobile Apps
Web 3.0 is an evolving concept that aims to enhance the security and privacy of mobile apps and online interactions in general. While Web 3.0 is still in development and its full potential is yet to be realized, it introduces several key technologies and principles that have the potential to improve security and privacy in the mobile app space. Here are some ways in which Web 3.0 can enhance the security and privacy of mobile apps:
1. Enhanced Security & Privacy
Web 3.0 has revolutionized the way mobile apps handle security and privacy, ushering in a new era of enhanced protection for users. With Web 3.0 technologies, mobile apps have become more decentralized, transparent, and resilient against malicious activities. One of the key features of Web 3.0 is the use of blockchain technology, which ensures immutability and tamper-proof records. By leveraging blockchain, mobile apps can provide robust authentication and identity management systems, eliminating the risks associated with centralized databases and vulnerable login credentials.
Additionally, Web 3.0 enables end-to-end encryption and secure communication channels, safeguarding user data from unauthorized access and interception. Smart contracts and decentralized protocols also play a vital role in Web 3.0, allowing for automated, trustless interactions and removing the need for intermediaries that often pose privacy concerns.
2. Empowering User Ownership & Control
A significant influence in giving people unprecedented ownership and control over mobile apps is Web 3.0. Users can truly own their data and digital assets thanks to Web 3.0’s decentralized technologies and protocols. Web 3.0, which has blockchain at its core, guarantees open and verifiable transactions, giving users total control over how mobile apps share and use their data. Users are given the ability to create and enforce the conditions of their interactions with mobile apps and other users thanks to smart contracts, which provide them with programmable ownership rights.
Decentralized storage systems also enable users to keep their data safely without relying on centralized servers, lowering the danger of illegal access and data breaches. Web 3.0 empowers people to have sovereignty over their digital life by moving the power balance from centralized entities to individual users. This promotes a more fair and user-centric mobile app environment.
3. Redefining App Monetization
By providing novel and inclusive strategies that benefit both app developers and consumers, Web 3.0 is altering the established forms of app monetization. Cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols have a huge impact on mobile app monetization strategy in the Web 3.0 era. Blockchain technology enables direct peer-to-peer transactions between users and developers without the need for middlemen, enabling transparent and auditable payment systems in mobile apps. Additionally, Web 3.0 introduces tokenization, where apps can leverage pre-existing cryptocurrencies or develop their own tokens to encourage user involvement and reward contributions.
Thanks to this, users may earn and sell tokens within the app ecosystem, which also gives them a sense of ownership. Decentralized app (dApp) marketplaces, where developers may sell their programs directly to consumers without platform constraints, are one example of a unique monetization model made possible by Web 3.0. Web 3.0 redefines app monetization in this new paradigm by promoting better justice, transparency, and financial inclusion.
4. Unlocking Interoperability & Collaboration
Mobile apps’ ability to collaborate and communicate with one another is being transformed by Web 3.0, ushering in a new era of interoperability. Web 3.0 promotes easy integration and communication across various apps independent of their underlying platforms or technologies through standardized protocols and open APIs. Mobile apps can take advantage of the strengths and capabilities of other apps thanks to interoperability, which strengthens the user experience overall and produces a tremendous network effect.
Decentralized marketplaces and platforms are also included in Web 3.0, which stimulates developer cooperation and innovation by enabling them to build on one another’s work and generate interconnected ecosystems. Web 3.0 enables mobile apps to work seamlessly together by dismantling the silos that previously prevented collaboration, opening up new opportunities, and fostering communal advancement in the digital sphere.
Challenges & Considerations
Web 3.0 presents several challenges and considerations for mobile app development. Here are some of the key ones:
1. Scalability & Performance
In the context of Web 3.0, the decentralized web, scalability, and performance pose important issues. With transparency and security, Web 3.0 applications built on blockchain and other distributed technologies seek to transform a number of industries. But the decentralized character of these technologies frequently comes at the expense of performance and scalability. Blockchain’s constrained transaction throughput and computational demands may cause delays and congestion. Scalability becomes increasingly important when new users join the network and the amount of data grows. The consensus techniques used by blockchain networks can also cause latency and have an impact on performance.
For developers and researchers working on Web 3.0 projects, finding a way to balance the requirement for decentralization with the need for effective and scalable systems is an ongoing problem. To overcome these problems and realize the full potential of Web 3.0, creative solutions and improvements are being investigated at different levels of the technology stack.
2. User Adoption & Education
In the context of Web 3.0, the decentralized web, there are substantial issues with user adoption and education. The paradigm change brought about by Web 3.0 from conventional centralized systems necessitates that consumers comprehend and accept the new ideas and technology at play. Due to Web 3.0’s decentralized nature, many users may be unfamiliar with terms like blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (dApps). To provide a seamless transition for users used to traditional online apps, user-friendly interfaces, and intuitive experiences must also be built.
For Web 3.0 to be widely adopted by users, it is essential to reduce the complexity of engaging with decentralized systems, clarify the value proposition, and allay security and privacy concerns. To develop educational materials, hold workshops, and cultivate a supporting ecosystem that enables people to comprehend, investigate, and take advantage of the promise of Web 3.0 technologies, a collaboration between businesses, academics, and communities is crucial.
3. Regulatory & Legal Implications
Regulatory and legal implications pose complex challenges in the realm of Web 3.0, the decentralized web. The decentralized nature of Web 3.0 technologies, such as blockchain development and smart contracts, introduces novel legal considerations that may differ from traditional centralized systems. The lack of centralized intermediaries and the global nature of these technologies can create jurisdictional challenges and ambiguities in terms of regulatory frameworks. Governments and regulatory bodies around the world are actively grappling with these challenges, seeking to strike a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding public interests.
Establishing clear and robust legal frameworks that address the intricacies of Web 3.0 while ensuring consumer protection, preventing fraud, and maintaining market integrity is crucial. Collaboration between policymakers, legal experts, technologists, and industry stakeholders is essential to navigate this evolving landscape and establish a regulatory framework that supports the growth and responsible development of Web 3.0 technologies.
Future Outlook of Web 3.0
The future outlook of Web 3.0 is highly anticipated, as it promises to revolutionize the digital landscape. Web 3.0, also known as the decentralized web, aims to create a more user-centric, secure, and interoperable online environment. It is built upon technologies like blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized networks, which provide enhanced privacy, ownership, and control over data. The future outlook of Web 3.0 is highly anticipated, as it promises to revolutionize the digital landscape. Let’s take a closer look at what are they.
Predicting the Trajectory of Web 3.0 & Its Impact On Mobile Apps
The trajectory of Web 3.0 points toward a transformative impact on mobile apps. With the integration of decentralized technologies, such as blockchain and smart contracts, mobile apps can become more secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship. Users can have greater control over their data, with the ability to verify and authenticate information without relying on centralized authorities. This opens up possibilities for peer-to-peer transactions, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, and the creation of trustless ecosystems directly on mobile devices. Web 3.0 can unlock new opportunities for innovation in mobile app development, enabling a more user-centric and privacy-focused experience.
Exploring Potential Use Cases & Innovations in the Near Future
The near future holds immense potential for Web 3.0, with numerous use cases and innovations on the horizon. One area of exploration is decentralized finance (DeFi), where Web 3.0 can revolutionize traditional financial systems. Through smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), individuals can engage in trustless lending, borrowing, and asset management directly from their mobile devices. This has the potential to democratize financial services, reduce reliance on intermediaries, and create more inclusive financial ecosystems. Additionally, Web 3.0 can bring about significant advancements in supply chain management. By leveraging blockchain technology, every step of the supply chain can be recorded, verified, and transparently shared.
Final Words
The advent of Web 3.0 has resulted in considerable advances in the realm of mobile app development. Mobile apps can become more safe, transparent, and more efficient with Web 3.0 technologies such as decentralized networks, blockchain, and smart contracts. The incorporation of Web 3.0 ideas into mobile app development has the potential to transform a variety of industries, from finance and healthcare to entertainment and e-commerce.
We should expect a new wave of innovative and user-centric mobile apps that value privacy, data ownership, and decentralized architectures as developers embrace the possibilities afforded by Web 3.0. The future of mobile app development in the Web 3.0 era is full of exciting possibilities, and it is crucial for developers to stay abreast of the latest trends and technologies to harness the full potential of this transformative landscape.





