The field of education has also undergone a significant transformation during the past few years. Today, what we once considered a “classroom education” looks very different. The educational sector is undergoing a transition as attention turns from rote learning of facts and figures to the development of critical thinking skills and the ability to understand complex ideas. How we educate students has become more important than what we teach them. Here is where technological advancements in education have really taken off.
According to research, the global EdTech (education technology) industry was worth USD 123.40 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to rise 13.6% from 2023 to 2030. It was predicted that by 2020, India’s EdTech market would be worth over $750 million USD. This sum is expected to surpass $4 billion by 2025 across the country.
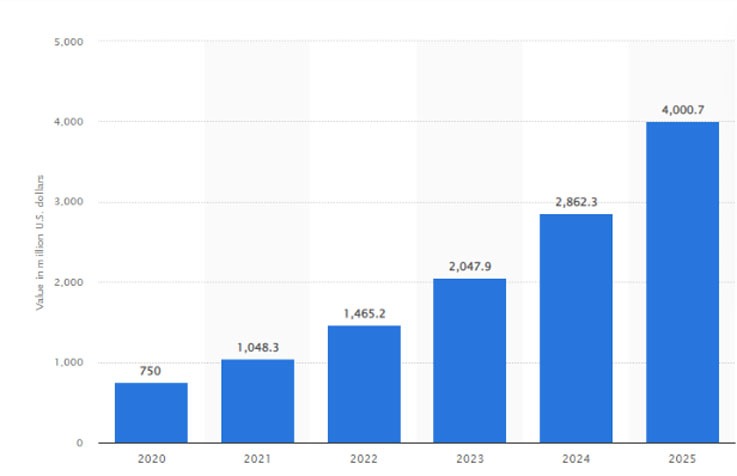
Image Source:- Statista
The original purpose for the development of the EdTech sector was to give students access to exciting multimedia lessons. Live lectures, cloud access, online laboratories, projects, and even online evaluations are some of the interactive options the e-learning sector has provided students with over the past five years. They facilitate students’ independent study and save time for instructors. Teachers’ time is also saved thanks to edtech because lessons may be tailored to each individual student. But what does the future hold for education in schools? Is EdTech destined to replace conventional schooling? Let’s find out.
Mobile and EdTech’s Growing Role in Education
Students have a better opportunity to learn when they are given the tools and resources they need to be successful, which is what educational technology does. The support that students require to thrive in the classroom and beyond is made available to them through the use of technology. This support can take the form of online resources as today every education sector is indulged in education and training software development that help explain complicated topics or interactive learning experiences that keep students interested. They include increased student engagement, support for a variety of learning styles, improved opportunities for collaboration, more access to real-time feedback for educators, and preparation for the future. The following are some of the reasons why technology plays a vital role in the educational process.
- Improves Innovation and Creativity
- Enhances Collaboration,
- Facilitates Communication,
- Teaches Students to Be Responsible Online
- Increases learning enjoyment
- Teaches students how to be future-ready
Potential Benefits of Mobile Apps in EdTech
Here are some of the most significant gains from implementing mobile apps in the classroom:
1. Modern Learning Techniques
When it comes to learning, students benefit greatly from educational mobile Apps that use a more psychological approach. Using hard exercises, puzzles, and instructional games, the app ensures that they fully grasp the topics. Most kids prefer learning through audio-visual means. They are enthused and ready to absorb new information because of the novelty of this learning environment.
2. Supports Personalized Learning
Personalized learning is one of the main advantages of technology in education. Students can obtain knowledge that is catered to their needs, interests, and learning style via online resources and educational applications. They are able to gain information that is important to their studies, work at their own pace, and repeat classes as necessary. This kind of individualized instruction can assist pupils in maintaining motivation and achieving greater outcomes.
3. 24/7 Access
Mobile applications are accessible 24/7, unlike in schools. There’s no need to stress about scheduling. A classroom can be found everywhere. App learning is relaxed learning, not learning that is time-bound. Most apps encourage parental control that is kid-friendly. Only when they are in the mood to learn should kids need to reach for the device. It is easily operated by young children.
4. Enhanced Interaction
According to experts, educational applications can improve parent-child interaction by fostering a more engaged environment for kids. The best strategy is to interact with the kids when they are utilizing apps. Mobile applications improve children’s propensity for interaction.
5. Comprehensive & Systematic Approach
With the use of education apps, students can evaluate what they have learned and the sources behind it, sparking their curiosity to learn more but doing it methodically so that they are aware of where to start and what to look up. This entire procedure aids students in learning through application rather than theory.
Advantages of Mobile Apps in EdTech
Mobile apps offer several advantages in the field of Education Technology (EdTech), let’s check what are they:
1. Accessibility
Learners are able to go at their own pace and study at their own leisure thanks to mobile apps, which give them access to learning materials anytime, anywhere, and on any device.
2. Personalization
Mobile applications have the potential to provide learners with individualized educational experiences that are catered to their specific requirements and areas of interest by utilizing features such as adaptive learning algorithms, personalized assessments, and targeted feedback.
3. Engagement
Apps for mobile devices provide users with learning experiences that are both interactive and immersive. These experiences leverage aspects such as gamification, multimedia, and social learning to boost learner engagement and motivation.
4. Collaboration
Learners are able to work together on assignments and communicate ideas in real-time thanks to mobile apps, which can make collaborative learning and group projects easier to organize and carry out.
5. Analytics
Mobile apps can gather and analyze data on the behavior and performance of learners, which can help instructors track the progress of their students, identify areas of difficulty, and change their teaching tactics accordingly.
6. Cost-effective
Mobile applications can be more cost-effective than traditional classroom-based learning methods because they eliminate the need for tangible learning materials and minimize the requirement for travel expenses. This makes it possible for mobile apps to replace traditional classroom-based learning methods.
Examples of Mobile Apps in EdTech
Most EdTech mobile phone apps designed for use in schools are effective tools for bettering educational opportunities for both students and teachers. You can find tens of thousands of educational apps for everything from maths and English to science and history in the App Store and the Google Play Store. We have mentioned the name of some of the best mobile apps in EdTech.
Integration of Mobile Apps in the Classroom
Mobile apps offer a practical and entertaining approach to improving learning, making them a wonderful complement to the classroom setting. Here are some strategies for incorporating mobile apps into the learning environment:
1. Interactive Learning
Mobile apps can be used to design engaging, interactive learning experiences that motivate engagement from students. Teachers can, for instance, build games that reinforce important concepts or quiz students using apps.
2. Personalized learning
Mobile apps can be used to design individualized learning experiences that take into account the needs and learning preferences of certain students. Individualized lesson plans, feedback, and progress tracking are all possible with apps.
3. Collaborative Learning
Apps for mobile devices can be used to make activities that need students to work together to learn, such as group projects and peer evaluations. Apps can be used to develop a variety of tools, including discussion boards, platforms for document sharing, and video conferencing software.
4. Assessment & Feedback
Apps for mobile devices can be used to provide feedback to students as well as assess their learning. The usage of apps allows for the creation of quizzes, examinations, and surveys, as well as the provision of immediate feedback to students.
5. Flipped Classroom
Using video lectures or other online resources before class, students can learn new topics. This is known as a flipped classroom technique. Access to readings from lectures, lecture notes, and other resources can be made available through apps.
How Mobile Apps are Being Used in the Classroom
Apps for students’ mobile devices are becoming increasingly common in the classroom. The flipped classroom concept and collaborative learning activities are two common examples of how mobile apps are being used to transform education. Students in a flipped classroom watch recorded lectures or read materials on their mobile devices before arriving at class. This gives individuals the freedom to learn at their own pace and makes room in the class for collaborative projects and discussions that can help cement what they’ve learned. Mobile apps like TED-Ed and Edpuzzle are frequently utilized in flipped classroom setups.
Moreover, global education is increasingly using mobile devices as teaching tools. Teachers hold smartphones at a rate 10% points greater than adults, according to a Pew Research Centre survey. They are advocating for iPads for all students and implementing bring-your-own-device regulations to include tech-savvy into their lessons.
Students are able to better communicate and work together during collaborative learning activities when they use mobile apps. Using a class messaging tool like Remind, a teacher can send updates and reminders to students, while a group of students can utilize shared document editing software like Google Docs to collaborate on a class assignment. Quizlet, Socrative, and Padlet are also widely utilized as mobile apps for group study.
Personalized Learning with Mobile Apps
The use of mobile apps as a means to deliver individualized instruction is gaining traction. Here are some examples of how EDtech provides a personalized learning experience:
1. Adaptive Learning Algorithms
Adaptive learning algorithms use machine learning to customize the learning experience to the needs and preferences of each individual learner. These algorithms analyze a variety of data points, including user behavior, performance, and progress, to provide personalized content, pacing, and difficulty levels.
2. Personalized Feedback
One of the most important aspects of personalized education is customized feedback. Learners can get instantaneous feedback through mobile apps, which can help them pinpoint problem areas and receive recommendations for future studies. Motivating students by pointing out their achievements is another benefit of personalized feedback.
3. Gamification
Gamification is a popular strategy used in many mobile apps to make learning more engaging and fun. Mobile apps can use game-like elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards to encourage learners to engage in the learning process. By providing a sense of achievement and competition, gamification can help learners to stay motivated and invested in their learning.
4. Personalized Content
Mobile apps can also provide personalized content to learners. For example, a history learning app can provide articles and videos based on the user’s interests and preferences. By tailoring the content to the user’s needs, learners are more likely to stay engaged and interested in the learning process.
Benefits of Personalized Learning
Personalized learning refers to a teaching and learning approach that takes into account the unique strengths, weaknesses, interests, and needs of each student. It involves tailoring instructional content, pace, and approach to match the individual learning style and preferences of each learner. Here are some of the benefits of personalized learning:
1. Increased Student Engagement
When students feel that their learning experiences are tailored to their individual needs and interests, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated to learn. This engagement can lead to higher levels of student achievement and success.
2. Enhanced Student Motivation
Personalized learning helps students to take ownership of their learning, and they feel more motivated to succeed when they have a sense of control and responsibility for their own learning.
3. Improved Learning Outcomes
Personalized learning can lead to improved learning outcomes because students are more likely to understand and retain the material when it is presented in a way that is relevant and meaningful to them.
4. Differentiated Instruction
With personalized learning, teachers can provide differentiated instruction that is tailored to the individual needs of each student. This allows for greater flexibility in instruction and can lead to more effective learning.
5. Increased Teacher Effectiveness
Personalized learning allows teachers to focus their time and energy on individual students, rather than trying to teach a class as a whole. This can increase teacher effectiveness and job satisfaction.
Mobile Apps & Education Accessibility
Mobile apps can play a crucial role in increasing education accessibility by providing a variety of tools and resources that provide personalized learning experiences. Here are some ways mobile apps can help:
1. Remote Learning
Mobile apps can offer access to educational materials and interactive lessons, allowing students to learn from anywhere with an internet connection. This is especially important for students who live in rural or remote areas, where access to traditional classrooms may be limited.
2. Assistive Technologies
Accessible learning is possible with the help of mobile apps that give a variety of features and resources. Educational content can be made more accessible for students with hearing or visual impairments by including features like text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and other accessibility tools in apps.
3. Personalized Learning
Students can benefit from using mobile apps since they allow them to learn in a way that best suits them. Education can be made more available and successful for all students through the use of data and analytics to provide personalized learning experiences based on a student’s strengths and weaknesses.
4. Collaborative Learning
Students can collaborate on group projects and assignments from different locations using mobile apps designed for this purpose. Students who are unable to attend standard classes or who have difficulty interacting with others may benefit from this.
Examples of Mobile Apps That Cater to Diverse Learning Needs

Challenges & Considerations for EdTech Mobile Apps
Mobile apps have become increasingly popular in EdTech due to their ability to provide personalized and interactive learning experiences to students. However, when implementing mobile apps in EdTech, there are a number of difficulties and factors that must be taken into mind. Below are some of these issues and challenges discussed:
1. Security & Privacy Concerns
Mobile apps are vulnerable to security threats and privacy breaches. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the mobile apps used in EdTech are secure and comply with data privacy regulations. This includes implementing security measures such as encryption and secure data storage, as well as obtaining consent from users before collecting their data.
2. Digital Divide
Not all students have access to mobile devices or the internet, which creates a digital divide in the classroom. It is important to consider how the use of mobile apps in EdTech can widen this gap and how to ensure equitable access to technology for all students.
3. Need for Teacher Training
Teachers may need training on how to effectively integrate mobile apps into their teaching practices. They may also need support in selecting and evaluating the quality of mobile apps and monitoring their student’s progress using these apps.
4. Technical Issues
Technical issues such as glitches or connectivity problems may arise when using mobile apps in EdTech. It is important to have contingency plans in place to address these issues and minimize disruption to the learning experience.
Examples of Ethical Considerations
Informed Consent
It is important to obtain informed consent from students and their parents/guardians before collecting and using their personal data. This includes informing them about the purpose of data collection, who will have access to the data, and how it will be used.
Data Security
Schools and educational institutions have a responsibility to protect student data from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. This includes implementing secure data storage, transmission, and disposal practices, as well as using appropriate encryption and access controls.
Anonymization & De-Identification
In some cases, it may be necessary to remove or obscure personally identifiable information (PII) from student data to protect their privacy. This can be achieved through anonymization or de-identification techniques that prevent individuals from being identified.
Data Sharing
When sharing student data with third parties, such as educational researchers or government agencies, it is important to ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect the privacy and confidentiality of the data.
Data Retention
Schools and educational institutions should have clear policies and procedures for the retention and disposal of student data. This includes determining how long data should be kept, how it should be disposed of, and who is responsible for overseeing the process.
Future of Mobile Apps in EdTech
Education is being transformed by mobile apps because they give students instantaneous access to a wealth of study materials. The potential of EdTech mobile apps is growing exponentially as technology develops. Some potential uses for mobile apps in the field of educational technology are as follows:
1. Virtual & Augmented Reality
Mobile apps can use virtual and augmented reality technologies to create immersive learning experiences. For example, students can explore historical sites, view scientific simulations, or participate in interactive language learning experiences. Augmented reality apps can also be used to provide students with real-time feedback and information as they explore their surroundings.
2. Artificial Intelligence
Mobile apps can leverage artificial intelligence to personalize learning experiences for individual students. AI-powered apps can analyze student data to create custom learning paths and provide tailored feedback. AI can also be used to create intelligent tutoring systems that can adapt to student’s learning styles and preferences.
3. Gamification
Gamification involves using game mechanics to motivate and engage students in learning activities. Mobile apps can use gamification techniques to make learning more enjoyable and interactive. For example, apps can reward students with points or badges for completing tasks, or create game-like simulations to teach complex concepts.
4. Collaborative Learning
Group projects and peer assessments are just two examples of how students can benefit from the use of mobile apps in the classroom. Tools like message boards, file-sharing sites, and video conferencing programs can all be built with the help of apps.
5. Personalized Learning
Mobile apps can create personalized learning experiences by adapting to students’ individual needs and preferences. Apps can use data analytics to track students’ progress and provide personalized feedback and recommendations. Apps can also leverage machine learning algorithms to create personalized learning plans that are tailored to each student’s strengths and weaknesses.
Examples of Potential Advancements in Mobile Apps in EdTech
Here are a few examples of potential advancements in mobile apps in EdTech:
1. Interactive Simulations
Mobile apps can offer interactive simulations that allow students to manipulate variables and explore concepts in a virtual environment. For example, a physics app could allow students to adjust the mass and velocity of objects and observe how they interact in different scenarios.
2. Virtual Classrooms
With the increasing prevalence of remote learning, mobile apps can provide virtual classroom environments that allow students to participate in live classes and collaborate with their peers. This can include features like video conferencing, chat rooms, and interactive whiteboards.
3. Adaptive Learning
Mobile apps can use machine learning algorithms to personalize the learning experience for each student, adapting the difficulty and pace of content to match their individual needs and learning styles.
4. Augmented Reality
Mobile devices can use augmented reality technology to create immersive learning experiences that blend the real world with digital content. For example, an app could use the camera on a phone or tablet to overlay educational information on top of real-world objects.
Conclusion
The use of mobile apps and educational technology (EdTech) is changing the face of education. They are making education more adaptable to each student’s unique needs, creating more exciting opportunities for learning, and preparing students for an employment sector that is always evolving. We can anticipate even more fascinating uses of mobile apps and EdTech to improve education in the future as technology develops. If you’ve noticed the change in the way students learn and are considering developing your own EdTech mobile app, it’s important to work with a reputable and established mobile app development company for the development process. You should hire a development team that can assist you make use of digital learning to solve a variety of educational problems.





