Businesses are banking on minimally viable products and quickly soliciting input from early adopters as part of a dynamic ecosystem where agility and speed are equally valued. Following the launch of the Minimum Viable Product (MVP), the development cycle is restarted to further validate the concept through further testing, product redesign, and any necessary course corrections, both little (iterations) and large (pivots).
However, new viewpoints are a rarity in most situations. This means that/ the assumptions summarised in a framework are typically based on the intricacies of nuance, such as a new feature or capability (business model canvas). New businesses need to differentiate themselves from the competition more than ever, and early adopters’ feedback is critical in doing so.
A minimum viable product (MVP) can be developed and released to the market much faster than a fully developed product. There are likely minimal products (MVPs) in the beginning, and they are the foundation of many of the most successful online enterprises today. It’s hardly surprising that many businesses started with an MVP as it helps business owners to increase their ROI in marketing and provides tremendous business success.
Here we looked at some of the most well-known businesses that, rather than building a product in the traditional, segregated method, published minimal viable products (MVPs) that could be quickly updated and eventually became market leaders.
A Brief Overview of Minimum Viable Product
MVP stands for “minimum viable product,” and it’s a product with just enough capabilities to validate an idea and draw in early adopter clients. The minimum viable product (MVP) is beneficial in fast-paced industries like software development, where the product team needs to gather customer feedback to make rapid iterations and improvements. The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is essential to agile development since the agile methodology is predicated on evaluating and iterating products based on user input.
The minimum viable product (MVP) is the release of a new product that allows a team to gather the most validated learning about customers with the fewest resources. The product team at a company may opt to create and deliver a minimal viable product because they want to:
- Have something out on the market as soon as feasible.
- Before investing much in a project’s development, see how it fares with actual customers.
- Find out how well the company’s messaging lands with its target audience.Having an MVP ready to go before investing too much time and money on a product concept might help your business save time and money in the long run.
Different Types of MVP
You should have a look at the different kinds of MVPs before we get to the instances. While one version of an MVP could work for one business, it won’t benefit another. Once you have a firm grasp of the business model and your needs have been defined, you may select the most appropriate MVP for your company.
1. Concierge MVP
Concierge MVPs don’t require you to build a product before you know if there’s a market for what you’re offering because you help people achieve their goals personally. That is to say; the users are led by the hand to the answer to their difficulty.
2. Landing Page MVP
A website that is used to bring potential customers. By creating a “minimum viable product,” or MVP, you may evaluate your product’s viability before investing too much time or resources into its development. Visitors can sign up for a newsletter or go straight to the checkout with one click.
3. Email MVP
Writing an email is more accessible than creating a product or a feature. If you already have a clientele, you can test the waters by manually crafting and sending emails to see how they are received. The value proposition offered isn’t compelling if recipients read the email but don’t take action.
4. Piecemeal MVP
An MVP is a stripped-down final product version that lacks polished features and a polished design. Since this is the case, creating an MVP with the resources at hand is prudent. Piecemeal MVP is the term for this type of Most Valuable Player. Here, an initial working version (MVP) is developed using all available resources rather than constructing everything from scratch.
5. Single-Feature MVP
Dropping down to the granular, feature-by-feature, The minimum viable product (MVP) method is used to verify the need for individual product features. Entrepreneurs can use it to try out new parts or see how well third-party integrations work.
Successful Startup Started With MVP
1. Facebook
In 2004, Mark Zuckerberg established Facebook, a social networking website that has since achieved phenomenal popularity. The basic idea behind the initial version of the minimal viable product was to make it easier for undergraduates at Harvard to communicate with one another. Users could publish messages on board by utilizing the platform, and the notion proved to be adequate to the point where you can enhance the venue with more complex features in the near future. Mark was ultimately responsible for Facebook’s development into what it is today.
2. Amazon
One of the most notable instances of a minimal viable product that made it large is the popular, personalized multipage shopping destination for individuals. Although not many people know it, Amazon began in the early 1990s as an electronic bookseller. People back then naturally had little faith in the internet. Thus it was unrealistic to expect an online store to sell “everything.” The creator, Bezos, however, had a dream of creating a global powerhouse. According to a report, Net sales from Amazon.com’s online stores and services have grown exponentially between 2004 and 2021. The global e-commerce giant reported about $470 billion in net sales in the most recent fiscal year, up from $386 billion the year before. Let’s take a look at the graph below.
Annual net sales revenue of Amazon from 2004 to 2021
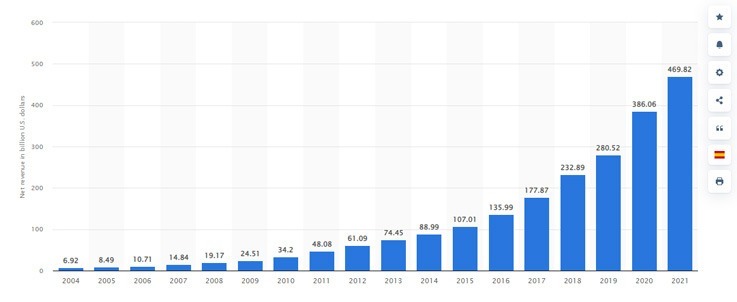
Image Source:- Statista
In the first round, we identified the best 20 goods for internet marketing and ultimately narrowed that list down to 5. However, Bezos determined that books were the best-selling digital item. The selling price, the number of volumes, and the worldwide interest in reading were all crucial variables. So he bought books in bulk from suppliers and began offering them for sale on an essential website at a discount. At the same time, most new business owners would have put their money into an established storefront. Bezos kept costs low and tested his notion with an essential website (MVP).
3. Instagram
By enabling users to share photographs and add filters, Instagram’s creator, Kevin Systrom, got an early sense of how the market would react to the app. The application was well received by its users. As a result, it has evolved to incorporate a plethora of ground-breaking new features, some of which include live broadcasting, direct messaging, company profiles, tales, hashtagging, and more. At this moment in time, 1,074,000,000 people are using Instagram all around the world. Let’s take a close look at leading countries based on Instagram audience size.
Leading countries based on Instagram audience size as of January 2022
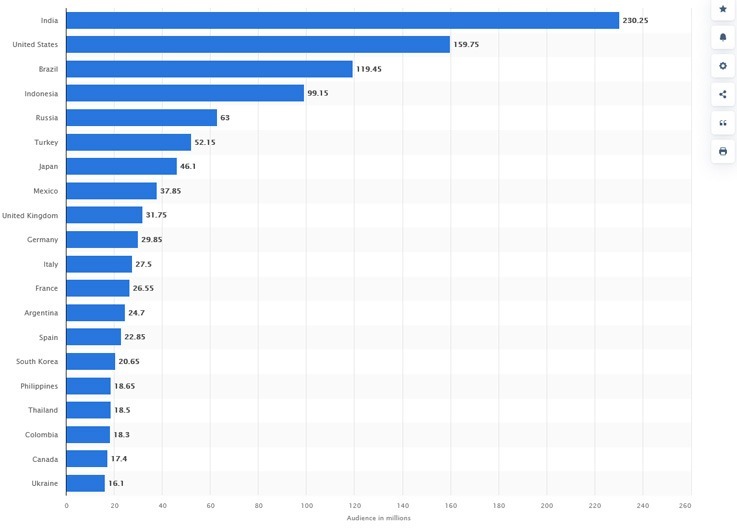
Image Source:- Statista
4. Groupon
Groupon was established in 2008 as a patchwork MVP that advertised the products and services offered by local companies and provided deals that were only valid for a limited amount of time. It was created with a clear concept: website visitors interested in receiving PDF versions of discount coupons may do so by subscribing to the service offered by Groupon. Groupon established the groundwork for the immensely successful worldwide platform that it is today by rapidly amassing a customer email list by soliciting its active site visitors for their input.
5. Dropbox
Dropbox is a fantastic file-hosting service founded in 2007 by MIT students Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi. It now offers its users a wide range of cloud capabilities, including personal clouds, client software, cloud storage, and file synchronization. The creators of Dropbox the idea for a cloud-based file synchronization service knew that putting the necessary hardware infrastructure in place would be a huge undertaking, both in terms of time and money.
So they took a baby step in the right direction and prepared a video (the MVP) to show potential investors what they could expect from the product once it was fully developed and released to the public. Despite its apparent lack of complexity, the film generated over 70,000 new signups from interested onlookers. In addition, the suggestions made were critical in making Dropbox what it is today. They also figured out how to hack Apple’s Finder so their icon would appear in the menu bar.
Similarly interested, Steve Jobs made an offer to purchase the business. Dropbox’s meteoric rise resulted from its founders answering the messy question, “How do you gather all your files, from all your devices, into one place?” despite numerous opportunities to sell the company in its early stages. It has tripled in size to 50 million users and now offers 100 GB of storage for $10 per month.
6. Zappos
An MVP is a minimum viable product that may be used to evaluate a market. In 1999, Zappos did this by selling shoes online without allowing customers to try them on first. Founder Nick Swinburn built a rudimentary website at shoesite.com after discovering the product’s commercial potential. Since Amazon spent a stunning $1.2 billion to acquire Zappos in 2009, it’s safe to assume that the MVP was wildly successful. The platform has experienced unprecedented growth since then, and it now earns over $1 billion in yearly income. Today, footwear is simply one of several things available from this company.
7. Airbnb
When Brian Chesky and Joe Gebbia, the creators of Airbnb, initially began the site in 2007, they were just two guys living in San Francisco struggling to make ends meet. To reach a satisfactory agreement, they devised the compromise of making the apartment’s penthouse available for guest use. As the minimal viable product, they published an advertisement on an entire website offering air mattress rental services.
After viewing the photographs of their accommodations, there was the speedy arrival of three guests. The concept’s validity was established, and a new framework was designed. Airbnb is now compiling information about local restaurants, sights, and events and displaying this data alongside guest reviews and ratings to provide a better service to its clients. This brand-new company has 4 million listings and a current market value of $30 billion.
8. Foursquare
Foursquare is a geosocial networking service that began as a single MVP in 2009. Earlier in the day, users may check in from different locations, share their experiences with friends and family, and earn badges for their efforts. People were just more enthusiastic about using the service because of the gamification elements, which required no special features or high-end design. This led to the product’s rising popularity, and as you know, Foursquare is today a global city directory used to find lodging, dining, nightlife, and more in many locations.
Final Words
For software development, the myth of a perfect business model has been supplanted by the minimum viable product (MVP) in a constantly evolving market. It dramatically reduces the risk of investing in a finished product and frees up time for companies to focus on adapting their products rapidly to the market. It’s also true that most successful MVPs don’t remain startups for too long.
Therefore, the most significant thing you can do if you are a cutting-edge entrepreneur needing MVP software development services is to join forces with the expert group. The company’s services for MVP product development are backed by years of experience in the field and may aid you in detecting mistakes and achieving quicker wins.





